Goods and Services Tax (GST) is the newest indirect tax regime in India. It is a value-added tax levied on the supply of goods and services across the country. As GST has already affected the Indian economy since 1st July 2017, it has changed the working style of every business. GST advantages and disadvantages are imperative to understand. GST benefits will enlighten you as to why GST is necessary. It has almost been a year since GST rolled out in India; hence it is imperative to understand the advantages and disadvantages of the GST law. Let’s look at some benefits of GST.
Advantages of GST
- One India- One Market: Before GST, there were some taxes which prevented India from becoming a common market. Whereas GST as a single tax, which is imposed all over a country on production, sales of goods and services; resulted in turning India into a common market.
- Single Point of Compliance: The whole compliance structure of GST is dependent on Information Technology (IT) system.gov.in is the web portal of the Government of India known as GST Common Portal where taxpayers can get access to all GST related facilities such as registration, returns, reports mismatch, e-way bill, etc. It is the single point of compliance, and now the taxpayers would not be required to visit different tax departments.
- Removal of ‘Cascading Effect’: Cascading effect simply means ‘tax on tax.’ In previous tax regime, when any goods were manufactured and sold to any wholesaler/retailer, excise duty was levied on the goods, and when such retailer sold these goods to any consumer, he used to levy VAT on the total value (including excise portion) of these goods. The retailer was not allowed to take input tax credit of the excise duty paid by him to the manufacturer, resulting in cascading effect and inflated value of goods for the consumer. Let us understand it by an example, in the given below case the total cost of goods for the wholesaler/retailer comes to Rs.112 (including excise amount Rs.12) because he was not allowed to set off this excise duty with VAT payable and thus, excise amount became part of his total cost value. Hence, Rs.1.5 (12*12.5%) is the cascading effect because vat of 12.5% was levied on excise duty of Rs.12 also.
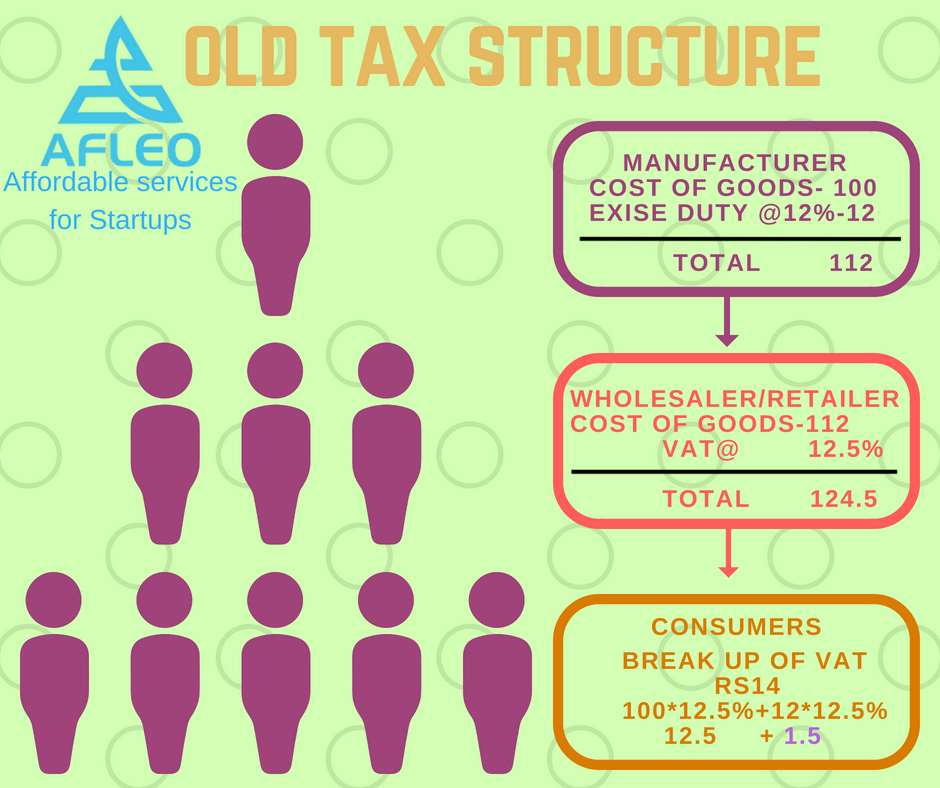
Thus by subsuming excise duties and VAT and other Central and State indirect taxes into a single tax and by allowing a set off of tax paid in the previous stage of a transaction would remove the effect of cascading.
- Obliteration of multiple taxes and avoidance of double taxation: All central government indirect` taxes such as central excise duty and additional excise duties, service tax, central sales tax, etc. and all state government indirect taxes such as state surcharges and cess, entertainment tax, VAT, entry tax, etc. are subsumed by a single tax GST, thus eliminating the issue of multiple taxation. For which you have to apply for GST Registration
Also, in the previous tax regime, there were some specific industry transactions which were taxed as goods as well as services. For example, a taxpayer providing restaurant services was required to pay service tax on such transaction considering it as a service and was also required to pay VAT on the same transaction considering it as the sale of goods, which lead to double taxation of the single transaction. Since GST is levied uniformly on goods and services, issues relating to double taxation would not arise.
- Seamless Flow of Goods across Nation: In the previous tax regime, while transporting goods from one state to another, CST (central state tax) and Entry tax were levied for entering into another state. The trucks transporting these goods had to pay entry tax while entering to every state border which was collected by individual states. Due to this, some manufacturers would avoid supplying their goods outside their own state. However, after GST rolled out, interstate transportation of goods became much easier as CST and Entry tax was replaced by a single tax, i.e., GST. It also resulted in the reduction in transportation cost.
- Ease of Doing Business: Before July 2017, a business person had to register with different tax authorities and file different tax returns. After GST came into existence, one was required to comply with only one single tax. Due to this, a business person can now focus on his business without worrying about different indirect taxes and laws.
- 0% tax on Essential Commodities: Essential commodities like fruits and vegetables, milk, salt, printed books, newspaper, grains, etc. are kept under the 0% tax rate slab under GST. Earlier some of these items were taxed in few states under VAT law. This is a major relief for the common masses
- Refund to Exporters: The refund process has been simplified under the GST regime. In case of exports, the genuine taxpayers are rewarded by getting an immediate refund, on the provisional basis, of 90% of their claim arising out of exports. The taxpayers need not visit any tax department for claiming a refund, a simple online refund process suffices, and the refund amount is directly credited to the taxpayers’ bank account.
These are the GST advantages and benefits of gst in India
Disadvantages of GST
- Adversity for Small Businesses: Every person having an aggregate turnover exceeding the limit of Rs. 20 Lakhs will be required to register under the GST Act. The registration limit is based on the turnover of the business and not on the profits or revenues earned. Thus a business entity having low-profit margins will still be required to comply with monthly GST processes. This would be tiresome for small businesses and at the same time, it would be a costly affair because a separate skilled person would be required for only GST compliance purpose, resulting in lower residual profits.
- Website Issues: Every normal registered person is required to file a minimum of 3 returns every month on or before the relevant due dates. At times, the GST portal is unable to handle the load on these due dates, resulting in site blocking or denial of access error. However, the Government is working to overcome such problems.
- Lack of Clarity: GST law is almost a year old now, but there are many rules and provisions of the Act, which still require a detailed clarification from the Government. The opinions given by the professionals and experts are subjective in nature. Thus the confusion still persists as to what would be the exact interpretation of the particular provision or rule in question.
- Lack of Computer Literacy: As the whole GST system is technology driven, it is very important for a taxpayer to be a computer literate in order to comply with GST law. The current GST system is a paperless system where compliance is done via GST online portal. The computer literacy rate among small businesses and traders is very low, which would result in a hindrance to the GST compliance process.
- Staff training costs and hiring experts: All businesses, whether large or small, will need to train their accountants and other staff to be GST compliant. GST, being a new tax, will necessitate the hiring of experts and proficient employees resulting in higher expenditure.
These are the GST disadvantages which make us think as to whether what are the points on which we need to introspect and improve.
Conclusion
These are the pros and cons of GST. GST law is still in its primary stage and will tend to have problems and issues. However, the Government is trying its best to simplify the GST compliance procedures and promptly addressing the issues.
Currently there may be many obstacles in GST path, whether it is an implementation of law or adaptation by people, but in the long run, GST would surely prove beneficial for each and every segment of the Indian economy.
For any queries regarding GST, please fill the form below.


1 thought on “Advantages and Disadvantages of Goods and Service Tax (GST)”
Keep up the great work! Thank you so much for sharing a great posts.
Comments are closed.