What is the Foreign Trade Policy?
The Foreign Trade Policy is the framework of strategy or the set of guidelines introduced by the Government of India to promote the export of goods/services from the country and generate employment by encouraging foreign trade. The Policy is notified by the Ministry of commerce and industry for the period of 5 years and updated on 31st March every year and comes to effect on 1st April.
The Current foreign trade Policy of India: FTP 2015-20
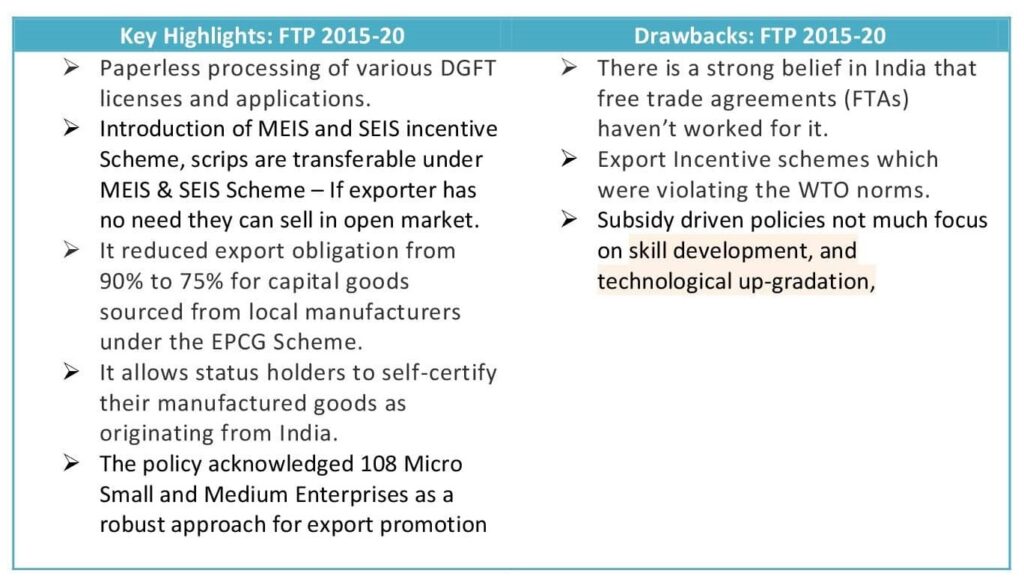
The Current foreign trade policy was introduced on 1st April 2015 for the period of 5 years and its primary objective was to facilitate trade by reducing transaction cost and time, making Indian exports competitive in Global Market. The Current FTP 2015-20 has been praised for several reasons because of its emphasis to promote the export through additional incentives and other measures, but it has faced a decent share of criticism also. Refer to the table below explaining the key highlights of FTP 2015-20 and drawbacks in the 2nd column.
Considering how badly the import-export industry has been affected by the ongoing pandemic Covid – 19. The Government had decided to stick with FTP 2015-20 till the 30the of September 2021 with a total extension of 18 months which was supposed to end on 31st March 2020. The new policy may come into effect from 1st October 2021.
New Foreign Trade Policy (FTP) 2021-26
The meeting was held on 12th January 2021 on the subject of “New Foreign Trade Policy for the year 2021-26” and the main mission for the policy would be to make India a leader in International Trade in the next 5 years as per the committee.
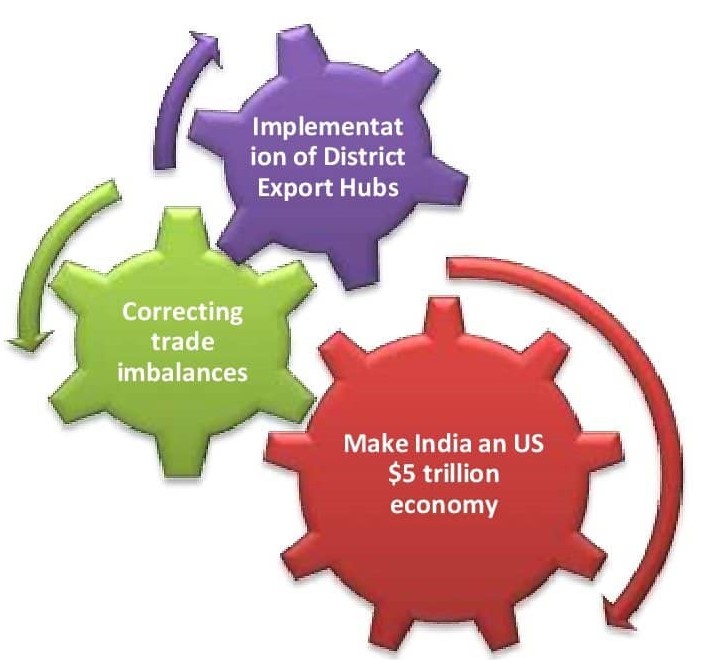
The Government seems committed to working seriously towards its $5 trillion dream, the Ministry of Commerce and Industry has few following plans for the new policy as briefed in the meeting with the committee. –
Targeting for $5 trillion economy- The Hon Prime Minister of India Shree Narendra Modiji has the vision of making the Indian Economy $5 Trillion by 2025 and appealed to the citizen to be “Vocal for Local” and “Be Local and Go Global”. To achieve the dream, India needs to register a GDP growth rate of 8% or more in the next few years and triple its exports to $1 trillion by 2025. The advisory group has suggested the reformation of labor laws, reducing the capital cost, selecting the right trading partner, sector-specific strategy to promote the export, etc
Implementation of District Export Hubs – The “District Export hub initiative” will be a significant part of the new policy which aims to help small businesses and farmers in providing export opportunities through eCommerce and digital marketing platforms. The following objective shall be fulfilled under this initiative.
- The Government will identify the potential goods and services in each district,
- Will identify the Agricultural and Toy Clusters,
- Set up district export promotion committees (DEPCs), which will make action plans to promote district export.
- Mapping of GI (geographical indications) products.
Correcting Trade imbalance- There is persistent demand from the industry to correct the imbalances in India’s International trade processes; discussion has been done to reduce the constraints in the global market regarding the policy and procedure of FTP, lower the transaction cost, and enhancing the ease of doing business.
Expectations from new policy FTP 2021-26
The Covid-19 had devastating consequences on International Trade and it is still affecting the industry and country experiencing a dramatic dip in both import and export. Though the situation is improving the road to recovery is not easy, and that is the reason a new foreign trade policy must deliver. Depending on the suggestions received from Import-Export industries, export promotion councils, some key expectations from Foreign trade policy 2021-2026 are discussed below –

WTO Compliant Policies – The Government has approved the Remission of Duties or Taxes on Export Products Scheme (RoDTEP) for the export of goods by replacing the previous scheme MEIS. The RoDTEP came in effect from 1st January 2021 and the rates are yet to be decided under RoDTEP.
Infrastructure Upgrade – Our neighboring country China is a Manufacturing and Export hub due to its network ports, highways, and high-speed trains, India needs to learn from it and needs to improve the infrastructure by upgrading the existing ports, warehouses, quality testing, and certification centers.
Digitalization – The FTP must be formulated to make the Import-Export process paperless and online with the help of digitalization for bringing transparency in global trade.
Easy Access to Credits –The exporters specifically MSMEs continuously asking for easy credit access as financial institutions like banks are reluctant to provide financial assistance due to lack of adequate collateral. The new policy must open up alternate credit avenues such as financial technology start-ups and need to raise the borrowing limits at the Export-Import Bank of India.
Awareness in Export – The Policies should be formulated so that they consist of awareness programs and workshops to aware the exporters about the international laws & market.
Tax Breaks – The New FTP must contain the policies for easing and lowering the tax rates by simplifying the import duty structure, i.e. high duties on finished goods and minimal duties on the raw materials.
Conclusion
The new FTP would play a vital role in achieving the target of a $5 trillion economy by 2025, with the proper strategic planning and effective implementation of all the policies and procedures India can be placed on the right path. To achieve the target India has to boost the export of both goods and services by systematically addressing domestic and global constraints by reducing the transaction cost, implementing WTO compliant policies, and enhancing the ease of doing business.
Before introducing the new foreign trade policy Government has taken various decisions such as the replacement of the MEIS Scheme with the RoDTEP Scheme which was not compliant with WTO norms, the extension of the ROSCTL scheme for garment exporters till March 2024.
The Ministry of Commerce has taken various measures to enhance the ease of doing business for Importers and Exporters have launched an online portal for – 24X7 auto Issuance of IEC, Online Platform for e-issuance of Preferential Certificates of Origin, Paperless issuance, and redemption of AA/EPCG License, helpdesk services for Exporters & Importers, E-issuance of licenses for import/export of restricted items, paperless processing and e-verification of the authenticity of DGFT issued documents.
The DGFT is continuously reviewing and simplifying the policy procedures based on exporters’ suggestions.
How Afleo can help you to get the maximum benefits from the FTP?
We at Afleo Consultants are India’s leading Export Import Consultants, having rich experience of 10+ Years in the domain. We specialize in all the DGFT related matters, Export promotion schemes such as RoDTEP, MEIS, SEIS, Advance License, EPCG, AEO certification, Star Export House certification, Duty Drawback, etc.
- We comprehend new schemes and all the policies under FTP, realizing the benefits for exporters and importers,
- Turning the policies into a simple form that is easily understandable to our clients.
- We have an experienced team working on understanding the foreign trade policies and finding the value it will add to our client base from various industries in the most effective manner.
- We assist our clients by updating them about the foreign trade policies to understand the value addition policy will bring for their benefit and guide them to avail all the benefits given under FTP.
[Not sure whether your company is taking all the Export incentives notified by the Govt? – Refer to our article on “18 latest Export promotion schemes/Export Incentives in India”]
We have a PAN India presence.
We would appreciate your comments and views on the above topic.
Have any doubts? Please fill the form below to get in touch with us.

