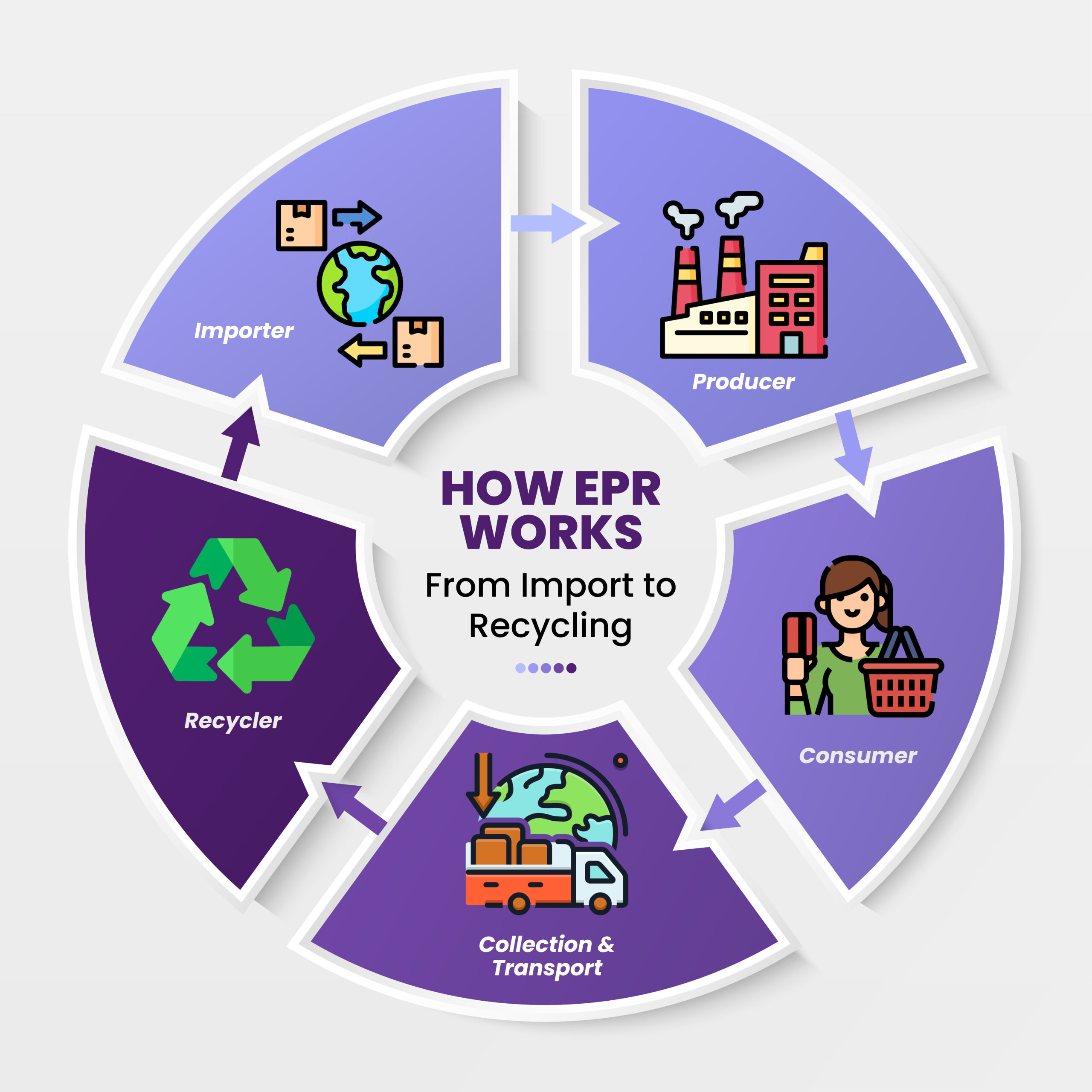
In the current international economy, it is not optional to be green – it’s a necessity. Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) is a powerful policy vehicle through which importers, producers, and proprietors are obligated to bear responsibility for the product’s environmental aspect, particularly where consumed or on end-of-life cycle.
For Indian importers, it has now become obligatory to obtain an EPR Certificate for Import in India under different waste management regulations. With changing rules and an increased thrust toward sustainability, particularly with 2025 updates on the cards, being compliant is of paramount importance for seamless operations.
In this blog, we will take you through all that you must know about the EPR Certificate for Import in India – meaning, process, documents needed, costs incurred, and compliance requirements.
What is an EPR Certificate?
The EPR Certificate is a government sanction issued by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), which permits the company to import, manufacture, and sell certain products on condition that they are responsible for the disposal of their waste upon consumption.
The fundamental goals of EPR are:
- Encouraging environmental sustainability through minimizing waste.
- Making producers responsible for the end-of-life disposal of products.
- Promoting recycling and reuse through organized waste management strategies.
Essentially, EPR puts the onus of waste management back on producers and importers rather than consumers and governments, promoting a circular economy.
[Read more Information regarding EPR for Plastic Waste]
Is an EPR Certificate Mandatory for Importers in India?
Yes, certainly. According to guidelines issued by the CPCB and in accordance with various rules for waste management (Plastic Waste Rules, E-Waste Rules, Battery Waste Management Rules, etc.), importers are required to procure an EPR Certificate prior to importing goods into India.
Non-compliance can result in:
- Heavy fines.
- Confiscation of goods at the customs.
- Revocation of import licenses.
- Legal proceedings under environmental legislation.
Importers that trade in electrical appliances, plastics, batteries, and tyres have to obtain EPR authorization to legally operate within India. And even other importers who do not trade in these items but import Items that are wrapped in plastic packaging or carry Bags or Plastic sheets or Like material are also required to obtain EPR for Plastic waste before Import consignments arrive at the Customs.
Goods That Need an Import EPR Certificate
EPR compliance is needed by importers handling the following categories of goods:
1. Plastic Waste
- Packaging items
- Single-use plastics
- Multi-layered plastics
- Plastic carry bags
- Any Item imported which is wrapped in any type of plastic packaging.
2. E-Waste
- Mobile phones, laptops, computers
- Televisions, refrigerators, washing machines
- Electronic gadgets and toys
- Printer cartridges, CFLs, LED bulbs
3. Battery Waste
- Lead-acid batteries
- Lithium-ion batteries (used for mobiles, EVs, etc.)
- Nickel-Cadmium batteries
4. Tyres
- Imported tyres (new and used)
- Rubber items intended for vehicle use
Other Waste Categories Under EPR (As per Latest Updates)
Apart from the above core categories, CPCB has also expanded EPR coverage to include:
- Used Oil Lubricant, base oils imported, manufactured, sold domestically.
- Construction and Demolition waste:
The debris part of the waste, such as, cement concrete, bricks, cement etc. shall be accounted for assessing the extended producer responsibility targets. - End of Life Vehicles:
scrapping targets of End-of-Life vehicles for vehicles the producer has introduced in the domestic market - Solar Waste:
Solar PV panels and modules are now under scrutiny for post-lifecycle disposal, with expected EPR mandates coming into force by 2025.
Tip: Stay updated by frequently checking CPCB notifications and Gazettes for category additions.
Documents Required for EPR Certificate for Import
Here is a checklist of documents required for a hassle-free application process:
- Company PAN Card & GST Certificate.
- Importer Exporter Code (IEC)
- MSME Certificate.
- Authorized Person’s PAN card.
- Image of imported item.
- Product Details and Specifications (catalogues, brochures)
- Import and sales data of last two Financial years.
- Electricity bill.
- Ownership proof like rent or lease agreement.
Pro Tip: Having all documentation in hand decreases the risk of rejection.
Format-Specific Tips
- Product Image: Include product label and packaging in the image to confirm plastic/electronic relevance.
- Import Data Format: Upload in Excel or CSV, categorized by HS Code, invoice number, weight (kg), and value (₹).
Process to Get EPR Certificate for Import in India
The EPR Certificate application is a uniform process:
1. Registration on CPCB Portal
Register an account on the official CPCB EPR registration portal.
2. Submit Required Documents
Upload all documents as required in the prescribed format.
3. Pay Applicable Fees
Online payment of registration/application fees.
4. Scrutiny and Evaluation
CPCB officials check the submitted information. Queries, if any, need to be answered immediately.
5. Grant of EPR Certificate
Upon successful verification, the EPR Certificate is granted.
EPR Certification Fees and Timelines
Fees:
- Fees differ based on the product category and company turnover.
- Generally ranges from ₹10,000 to ₹1,00,000 and above for large importers.
- Some categories include extra environmental compensation charges.
Timelines:
- Application Processing: 30-90 days
- Certificate Validity: 1-3 years, depending on product type and rules.
- State-specific variations: Some states may require extra documentation through SPCB even if CPCB clearance is achieved.
How EPR Targets Are Calculated
The target calculation for each type of EPR is different but it intends to capture the waste generated by the obligated entities.
For plastic packaging CPCB assigns targets based on:
- Weight and type of packaging material used (in MT).
- Recycling milestones (e.g., 70% recycling of plastic waste in Year 2).
Example: If you had imported around 10 MT of plastic packaging with the goods in FY 2023-24 and 14 MT in 2024-25, your target for 2025-26 would be around 6 MT (50% of average of two years).
Post-Certification Compliance & Renewal
Once they get the EPR Certificate, importers need to do the following:
- Annual Reporting: File EPR compliance reports to CPCB.
- Waste Collection Targets: Attain recycling goals (sales volume percentage).
- Renewal: In most cases like Plastic EPR the registration does not need to be renewed but failure to adhere to the obligations, might result in revocation of the registration.
- Avoid Cancellation: Non-conformity would lead to cancellation or suspension of the EPR sanction.
Being ahead in compliance causes no disruption to business.
Common Mistakes to Avoid During CPCB EPR Application
- Submitting expired electricity or rent agreement documents.
- Uploading images of products without packaging.
- Ignoring CPCB email queries (leads to auto-rejection).
- Figuring out the entity type (Producer, Importer, Brand Owner, Recycler, Seller etc)
- Mentioning quantities precisely taking into consideration the expected information and the unit
Benefits of EPR Certificate for Importers
Attaining an EPR Certificate presents several benefits:
- Legal Compliance: Prevents fines, product seizures, and litigation.
- Smooth Customs Clearance: Simplifies the customs process through EPR documentation.
- Enhanced Brand Reputation: Places the brand with environmentally friendly practices, enhancing customers’ trust.
- Sustainability Leadership: Makes your brand a green leader.
- Business Stability for the Long Term: Future-proofs your business against changing regulations.
Alignment with Global ESG Goals
Having an EPR certificate enhances your ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) profile, making your business investment-friendly and internationally credible.
- Supports UN SDG 12 – Responsible Consumption and Production.
- Builds trust with foreign clients and investors focused on sustainable supply chains.
Common Challenges and Expert Tips
Applicant challenges:
- Incorrect Document Submission: Incompatible or lacking paperwork.
- Portal Glitches: System glitches on the CPCB portal that slow down submission.
- Selecting the Wrong Consultant: Hiring inexperienced consultants results in rejections.
Expert Tips:
- Always cross-verify documents.
- Have scanned copies ready in high resolution.
- Get your entire registration done smoothly by an experienced consultant like Afleo.